들어가며
NLP관련 논문들을 읽다보면 다양한 NLU/NLG 태스크와 데이터셋이 등장한다. 이에 대해 모르면 모델이 어떤 태스크에 장점이 있는지 알기 힘들뿐더러, 데이터셋을 특정 태스크에 맞게 조작하거나, input을 변형해야 할 때 도움을 받기 힘들다. 따라서 직접 모델을 구축하고 input을 넣을 때 inductive bias를 준다거나, implementation detail을 만드는게 까다로울 때가 있다. 아직까진 한국어로 정리된 자료가 없는 것도 같으니 논문을 읽으면서 한번쯤은 봤던 데이터셋과 태스크를 정리해보도록 하자.
LAMBADA
LAMBADA는 (Paperno et al., 2016) Language Model을 평가하기 위한 데이터셋이다. 텍스트 내 긴 문장에 대한 의존성을 테스트하기 위해 문장의 마지막 단어를 예측하는 것을 목표로 한다.

GLUE (General Language Understaing Evaluation)
GLUE는 NLU 시스템을 평가하기 위해 모아놓은 9개의 데이터셋이다. Task는 하나의 문장을 분류하는 태스크와 두 쌍의 문장을 분류하는 태스크로 이루어져있다.
GLUE 개발자들은 training/dev 데이터셋과 제출서버, 리더보드를 제공하여 비공개 test 데이터를 통해 참가자들이 경쟁할 수 있다.
GLUE에는 아래와 같은 종류의 데이터셋이 포함되어 있다.
| task | 설명 |
|---|---|
| Multi-Genre Natural Language Inference (MNLI) | 다양한 장르에 대해 크라우드 소싱을 통해 얻은 라지스케일의 entailment classification task이다. 한 쌍의 문장에 대해, 두 번째 문장이 entailment인지, contradiction인지, neutral인지 분류하는 문제 |
| QQP (Quora Question Pairs) | Quora에 올라온 질문들이 의미적으로 비슷한지 분류하는 문제 |
| QNLI (Question Natural Language Inference) | Stanford Question Answering Dataset의 이진분류 버전으로, positive example (question, sentence) 쌍은 올바른 정답을 포함하고 있고, negative example (question, sentence) 쌍은 정답이 없다. 원래 Stanford Question Answering Dataset은 question-paragraph 쌍으로, paragraph내 sentence 중 하나는 이에 대한 정답을 갖고 있다. QNLI는 이 paragraph를 여러 sentence로 나눈 버전 |
| SST-2 (Stanford Sentiment Treebank 2) | 영화 리뷰에 대한 문장의 긍/부정을 판별하는 sentiment analysis |
| CoLA (The Corpus of Linguistic Acceptability) | 문장에 대한 이진분류로, 영어 문장이 언어적(linguistically)으로 문법적으로 옳은지 판단 |
| STS-B (Semantic Textual Similarity Bench-mark) | 뉴스 헤드라인과 그 외 소스에서 뽑은 문장 쌍으로, 두 문장의 유사도에 따라 1부터 5까지 판단 |
| MRPC (Microsoft Research Paraphrase Corpus) | 온라인 뉴스로부터 뽑은 문장 쌍으로, 문장이 의미적으로 유사한지를 판단 |
| RTE (Recognizing Textual Entailment) | 이진 entailment task로, MNLI와 비슷. 그러나 학습 데이터량이 훨씬 작음 |
| WNLI (Winograd NLI) | 작은 NLI 데이터 셋으로, 대명사가 포함된 문장을 읽고 대명사가 무엇인지 파악하는 task |
Single-Sentence Tasks
COLA
SST-A
Similarity and Paraphrase Tasks
MRPC
SST-B
QQP
Inference Tasks
RTE
MNLI
WNLI (Winograd Schema Challenge)
WNLI:
NLI-format의 데이터는 작업하기가 까다로우므로 이 대신 SuperGLUE의 WNLI를 사용한다. WNLI는 query 대명사와 참조의 span을 제공해준다. Kocijan et al. (2019)에서 사용한 margin ranking loss을 이용하며, 인풋 문장은 spaCy를 사용하여 명사구를 추출한다. 그러나 이런 방법을 사용할 경우 데이터의 절반 가까이 사용할 수 없다는 단점이 생긴다.
QNLI (The Stanford Question Answering Dataset)
최근 GLUE 리더보드 결과들을 살펴보면 pairwise ranking formulation을 사용한 것을 볼 수 있다. pairwise ranking formulation는 학습셋으로부터 후보 답변들을 모은 뒤 이들끼리 비교, 하나의 (question, candidate)를 positive로 분류하는 기법이다 (Liu et al., 2019b, a; Yang et al., 2019 (XLNet)). 그러나 이러한 방법은 태스크를 매우 간단하게 만들 순 있지만 BERT와의 직접적인 비교는 어려워진다. 따라서 test set에 대해 pairwise ranking formulation를 사용하고, BERT와의 공정한 비교를 위해 dev set은 순수한 classification 문제로 만들어 푼다.
SuperGLUE
common sense reasoning
Common sense reasoning tasks are intended to require the model to go beyond pattern recognition. Instead, the model should use “common sense” or world knowledge to make inferences.
Winograd Schema Challenge
Natural Language Inference (NLI) / Recognizing Textual Entailment (RTE)
Natural Language Inference(NLI)는 두 문장 사이의 관계를 이해하는 능력을 측정한다. 보통 두 개에서 세 개의 클래스를 분류하는 문제로 구성되며, 모델은 두번째 문장이 논리적으로 첫번째 문장 뒤에 올 수 있는지, 이에 반대되는지, 아니면 참인지 (자연스러운지) 분류한다.
The terms Natural Language Inference (NLI) and RTE are often used interchangeably. Many papers begin by explicitly mentioning that these terms are synonymous (Liu et al., 2016; Gong et al., 2018; Camburu et al., 2018).
Textual Entailment Recognition has been proposed recently as a generic task that captures major semantic inference needs across many NLP applications, such as Question Answering, Information Retrieval, Information Extraction, and Text Summarization. This task requires to recognize, given two text fragments, whether the meaning of one text is entailed (can be inferred) from the other text.
RTE, STS, MRPC의 경우엔 MNLI single-task model에서 fine-tuning하는게 RoBERTa를 fine-tuning하는 것보다 더 좋은 것으로 나타났다.
SNLI
SNLI와 MNLI에 대해 학습된다. SNLI는 570,000개의 문장 쌍이 주어지며, 레이블은 contradiction, eintailment, neutral로 주어진다.
MNLI
MNLI는 430,000의 문장 쌍으로 구성되며, 대화부터 글까지 여러 장르를 포함한다.
RTE, STS, MRPC의 경우엔 MNLI single-task model에서 fine-tuning하는게 RoBERTa를 fine-tuning하는 것보다 더 좋은 것으로 나타났다.
Adversarial Natural Language Inference (ANLI)
- Paper: Adversarial NLI: A New Benchmark for Natural Language Understanding
- Repo: facebookresearch/anli
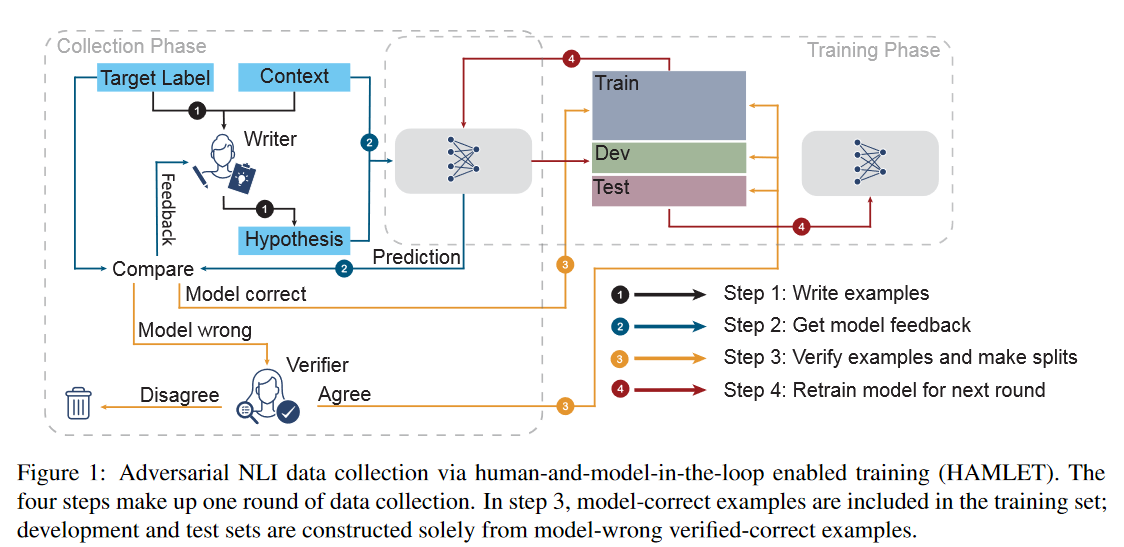
ANLI는 FAIR에서 개발한 데이터셋 및 데이터셋 구축 절차로, 기존의 NLI가 모델에 의해 쉽게 정복되는 현상을 방지하고, 오래 버티도록 설계된 데이터셋이다. AI가 사람 수준까지 정복되는데 MNIST는 15년, ImageNet은 7년 정도의 시간이 걸린 반면, NLU에서는 모델의 발전에 따라 쉽게 무너지고 있다. 특히 BERT의 발전 이후 GLUE같은 데이터셋 너무나 쉽게 무너져서 SuperGLUE 데이터셋의 필요성을 야기하였다.
ANLI는 벤치마크 데이터셋의 수명과 견고성 문제를 해결하는 NLU 데이터셋 수집을 위한, 반복적이고, 적대적인 human-and-model-in-the-loop solution을 제공한다. 즉, 다음과 같은 것을 목표로 한다.
The primary aim of this work is to create a new large-scale NLI benchmark on which current state- of-the-art models fail.
주의할 점은 본 ANLI는 데이터셋을 제공하는 것 뿐만 아니라 좋은 데이터셋 수집을 위한 절차를 제공한다는 것이다. 아래는 ANLI 논문에서 밝히고 있는 contribution이다.
1) We introduce a novel human-and-model-in-the-loop dataset, consisting of three rounds that progressively increase in difficulty and complexity, that includes annotator-provided explanations. 2) We show that training models on this new dataset leads to state-of-the-art performance on a variety of popular NLI benchmarks. 3) We provide a detailed analysis of the collected data that sheds light on the shortcomings of current models, categorizes the data by inference type to examine weaknesses, and demonstrates good performance on NLI stress tests.
첫 단계에서는 human annotator가 현재 최고의 모델이 정답을 맞추지 않게끔하는 example을 고안해낸다. 이를 통해 모델의 취약점을 포함하는 hard example을 생성하게 되고, 이를 training 셋에 포함하여 학습한 후 더 좋은 모델을 만들어낸다. 그후 강화된 모델을 대상으로 같은 절차를 진행하고, 몇개의 라운드를 통해 약점을 수집한다. 각 라운드가 끝날 때마다 새로운 모델을 학습시키고, 따로 test set을 마련한다. Never-ending learning (Mitchell et al., 2018) 세팅처럼 계속해서 반복적으로 이 절차를 진행하고, test 셋은 매 라운드가 지날 때마다 점점 어려워진다. 따라서 데이터셋은 현존하는 벤치마크보다 어려울뿐만 아니라, 정적인 벤치마크가 언젠가는 정복되는 것과는 다르게 “앞으로 전진하는”, NLU 시스템에 대한 동적인 목표가 되는 것이다.
Generation task
abstractive question answering and summarization
Reading comprehension
Most current question answering datasets frame the task as reading comprehension where the question is about a paragraph or document and the answer often is a span in the document. The Machine Reading group at UCL also provides an overview of reading comprehension tasks.
http://nlpprogress.com/english/question_answering.html#reading-comprehension
Semantic Textual Similarity
Reimers et al., 2016에 따르면 Pearson correlation의 경우 STS에 부적합함.
RTE, STS, MRPC의 경우엔 MNLI single-task model에서 fine-tuning하는게 RoBERTa를 fine-tuning하는 것보다 더 좋은 것으로 나타났다.
SICK
SentEval
SentEval은 sentence embedding의 품질을 측정하는 도구로, logistic regression classifier의 feature로 sentence embedding을 사용한다. 그 후 logistic regression classifier를 다양한 태스크에 10-fold cross-validation setup로 학습한 뒤 test-fold로 테스트를 진행한다.
그러나 SBERT의 sentence embedding은 다른 태스크에 대한 transfer learning을 위해 개발된 것이 아니며, 이보다는 fine-tuning BERT가 모든 레이어에 대해 업데이트를 진행하므로 새로운 태스크에 더 적합하다고 볼 수 있다. 다만 SentEval를 통해 여러 태스크에 대한 SBERT sentence embedding의 품질에 대한 인상정도는 남길 수 있을 것으로 기대하였다.
따라서 SBERT sentence embedding과 다른 embedding method를 아래와 같은 7개의 SentEval transfer tasks로 비교해보자 한다.
- MR: 별점 5점으로 측정된 movie reviews snippets에 대한 감정분석
- CR: 제품 리뷰에 대한 감정분석
- SUBJ: 영화 리뷰와 요약 플롯에 대한 Subjectivity prediction
- MPQA: newswire 데이터에 대한 Phrase level의 감성분석
- SST: Stanford Sentiment Treebank에 대한 이진분류
- TREC: TREC에 대한 fine grained question-type classification
- MRPC: Parallel news sources에서 추출한 Microsoft Research Paraphrase Corpus
Intent Detection
Intent Detection is a vital component of any task-oriented conversational system. In order to understand the user’s current goal, the system must leverage its intent detector to classify the user’s utterance (provided in varied natural language) into one of several predefined classes, that is, intents. However, the performance of intent detection has been hindered by the data scarcity issue, as it is non-trivial to collect sufficient examples for new intents. How to effectively identify user intents in few-shot learning has become popular.
Intent Classification
Intent Classification is the task of correctly labeling a natural language utterance from a predetermined set of intents.
CLINC150
150개의 의도와 은행, 여행 등 10개 분야로 분류된 22,500개의 쿼리로 이루어졌다. 또한, 범위를 벗어난 쿼리도 1,200여개 존재하며 oos (out-of-scope)에 속한다.
데이터셋 구축 과정